The first of two engravings of a
medieval and highly mysterious stone worm contained within a late 17th-Century
book by Eberhard Werner Happel
There are a number of mysterious and controversial biblical
creatures with potential relevance to cryptozoology, of which the most famous examples
are undoubtedly Leviathan and Behemoth (click here
and here to see my ShukerNature
investigations of them). Much less famous but no less remarkable than those two,
however, is the small yet highly intriguing subject of this present ShukerNature
post - the shamir.
Also spelled 'samir' or 'schamir', this is the Hebrew
name given to a tiny worm-like creature referred to in certain Jewish holy
books, including the Midrashim and the Talmud (particularly the Gemara – the
component of the Talmud that consists of rabbinical analysis of, and commentary
upon, an earlier work known as the Mishnah).
The shamir as depicted within the
Rosslyn Missal (an Irish manuscript dating from the late 13th or
early 14th Century)
According to Jewish tradition contained within
these and other sources, the shamir was one of ten miraculous items created by God at twilight upon the
Sixth Day of the Hexameron (the six days of Creation). Although it was only the
size of a single grain of barley corn, the shamir was so incredibly powerful
that merely its gaze was sufficient to cut through any material with ease, even
through diamond itself, the hardest substance on Earth. Such a wondrous
creature needed to be safeguarded, so God entrusted the shamir to the
hoopoe (or woodcock or moorhen, depending upon which version of the legend is
consulted), commanding this bird to protect the shamir from all harm.
In order to contain this mighty if minuscule worm,
the hoopoe placed it among a quantity of barley corns, then wrapped them all up
together in a woollen cloth, which in turn was placed inside a box fashioned
from lead – the only material strong enough to contain the shamir effectively
but without disintegrating from the intensity of its laser-like gaze. So here, safely
and comfortably ensconced within its leaden domicile, which was retained by the
hoopoe in the Garden of Eden, it passed through all the ages that followed.
Only once did the shamir emerge – during the time
of Aaron and Moses, when God commanded the hoopoe to lend this worm to Him for
the etching of the names of the 12 tribes of Israel upon the precious stones on
12 special priestly breastplates (the Hoshen), one breastplate for each of the
tribes and each breastplate composed of a different stone. The task was a very
difficult one, but when these stones were shown in turn to the shamir this astonishing creature accomplished it so expertly that not a single
atom of precious stone was lost or destroyed.
After this, the shamir was placed back inside its
lead casket, entrusted once more to the hoopoe's care, and there it remained,
in undisturbed obscurity – until the time of King Solomon the Wise. Solomon
wished to erect a glorious temple, but he was very mindful of God's
instructions, laid down long ago to Moses, that no place of worship, not even
an altar (let alone a temple), should be constructed using any tool made from
iron - because iron was a substance of war, and that if anything related to war
should ever touch a place of worship, it would be instantly and irrevocably
defiled. But if Solomon could not use iron tools, how could the stones needed
for constructing his temple be hewn?
An etching of the famous and
much-exhibited model of Solomon's Temple created during the 1600s by Rabbi
Jacob Jehudah Leon, which measured 80 ft in circumference and 13 ft high, and
was based upon information contained within the Bible's Book of Kings, Book
of Samuel, and Book of Chronicles
In an attempt to solve this riddle, Solomon
enquired far and wide, and eventually he learnt about the incredible
stone-searing shamir. Determined to utilise its extraordinary power, Solomon
dispatched a servant to seek out this wonderful creature and bring it back to
him. After a long search, the servant succeeded, and Solomon duly employed the
shamir to cut the rocks required for building his celebrated temple – the First Temple in Jerusalem. But that is where the story ends abruptly –
because after this magnificent edifice was completed, the shamir allegedly lost
its power, then vanished, and has never been heard of again…or has it?
In his engrossing book Sacred Monsters (2nd edit., 2011), Rabbi Natan Slifkin wondered if the shamir might have been based upon a real but not particularly well known creature native to the Negev Desert - the rock-eating snail Euchondrus, represented there by three closely-related species, E. albulus, E. desertorum, and E. ramonensis. Less than half an inch long, these mini-molluscs eat lichens that grow beneath the surface of rocks, and use a toothed tongue-like organ known as the radula to rasp away the intervening rock with great ease and rapidity. However, if such snails were indeed the identity of the shamir, surely the holy books and scriptures would have alluded to their shells? Yet no mention of any such structure possessed by the shamir exists. Also, these sources state categorically that the shamir does not destroy any portion of the rocks or precious stones that it cuts through, unlike the activity of these snails.
Intriguingly, there is an alternative school of thought postulating that the shamir was not a living creature at all, but rather a mineral itself, specifically an exceptionally hard green stone, which could cut through all other substances. Yet this identification fails to explain how the stones needing to be cut could be by merely being shown to the shamir, i.e. without the shamir making any direct contact with the stones, using only its gaze to achieve its appointed task. As noted by Rabbi Slifkin, however, one maverick scientist proposed an extremely ingenious, and plausible, solution to this dilemma. Immanuel Velikovsky (1895-1979) is best-remembered for his highly controversial theories of global catastrophic events producing profoundly revised datings of major events in ancient history, as propounded in bestselling books such as Worlds in Collision (1950) and Earth in Upheaval (1955). Turning his attention to the shamir enigma, Velikovsky suggested that perhaps it was a radioactive substance, which could certainly explain some of the most notable riddles encompassing it.
For instance: such a substance could produce its effects upon other substances merely by having them placed near (or shown) to it, not requiring direct contact with them. Also, what better container for a radioactive substance to be housed safely inside than a casket of lead, which would very effectively shield its potent effects? And as its radioactivity would diminish with time (i.e. its half-life), this could explain why the shamir's potency had ultimately faded away by the time that King Solomon's temple had been completed. If it were truly a living creature, however, the shamir's abilities could not be explained by any such theory.
In any event, I had always assumed that this incredible entity was entirely mythical – until 28 November 2013, that is, when Facebook friend Robert Schneck very kindly brought to my attention an astonishing but hitherto exceedingly obscure mystery beast that seemed at least on first sight to be a veritable shamir of the Middle Ages. Robert revealed to me two engravings of bizarre-looking beasts known as vermes lapidum or stone worms, and which had appeared in a hefty German tome authored by Eberhard Werner Happel and entitled Relationes Curiosae, oder Denckwürdigkeiten der Welt, which was originally published in five volumes between 1683 and 1691.
Intriguingly, there is an alternative school of thought postulating that the shamir was not a living creature at all, but rather a mineral itself, specifically an exceptionally hard green stone, which could cut through all other substances. Yet this identification fails to explain how the stones needing to be cut could be by merely being shown to the shamir, i.e. without the shamir making any direct contact with the stones, using only its gaze to achieve its appointed task. As noted by Rabbi Slifkin, however, one maverick scientist proposed an extremely ingenious, and plausible, solution to this dilemma. Immanuel Velikovsky (1895-1979) is best-remembered for his highly controversial theories of global catastrophic events producing profoundly revised datings of major events in ancient history, as propounded in bestselling books such as Worlds in Collision (1950) and Earth in Upheaval (1955). Turning his attention to the shamir enigma, Velikovsky suggested that perhaps it was a radioactive substance, which could certainly explain some of the most notable riddles encompassing it.
For instance: such a substance could produce its effects upon other substances merely by having them placed near (or shown) to it, not requiring direct contact with them. Also, what better container for a radioactive substance to be housed safely inside than a casket of lead, which would very effectively shield its potent effects? And as its radioactivity would diminish with time (i.e. its half-life), this could explain why the shamir's potency had ultimately faded away by the time that King Solomon's temple had been completed. If it were truly a living creature, however, the shamir's abilities could not be explained by any such theory.
In any event, I had always assumed that this incredible entity was entirely mythical – until 28 November 2013, that is, when Facebook friend Robert Schneck very kindly brought to my attention an astonishing but hitherto exceedingly obscure mystery beast that seemed at least on first sight to be a veritable shamir of the Middle Ages. Robert revealed to me two engravings of bizarre-looking beasts known as vermes lapidum or stone worms, and which had appeared in a hefty German tome authored by Eberhard Werner Happel and entitled Relationes Curiosae, oder Denckwürdigkeiten der Welt, which was originally published in five volumes between 1683 and 1691.
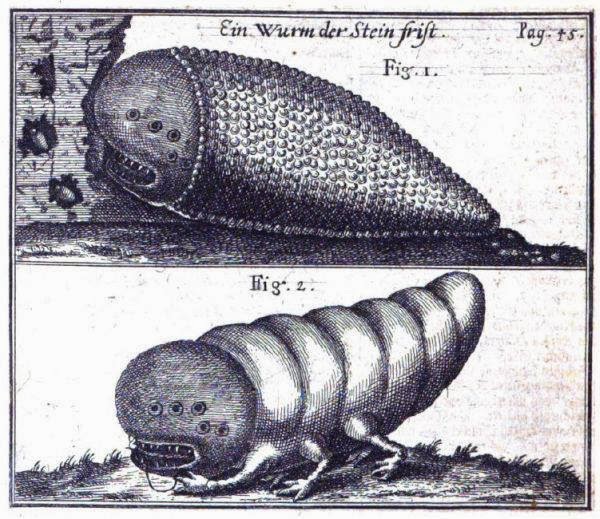
Two engravings of alleged stone worms
from Happel's Relationes Curiosae, oder Denckwürdigkeiten der Welt
According to Happel, the stone worms had originally
been brought to public attention by a 17th-Century monk called de la
Voye, from a Normandy monastery, who in 1666 had written a letter to a
Lord Auzout describing his remarkable discovery. One day, de la Voye had found
some of these very small, decidedly odd-looking creatures moving about incessantly
inside some holes of their own making in an old wall, much of whose rocky
composition had allegedly been eaten away and converted into dust by the
devouring nature of the worms. When he pulled out some of them and examined
them under a magnifying glass, the monk observed that they were each the size
of a single barley corn (the very same description, intriguingly, as used in
the Jewish holy books for the shamir) and enclosed in a grey shell, as depicted
in the first (labelled Fig. 1) of the two engravings presented above. As quoted
by Happel in his book, the monk continued his account of the stone worms in his
letter to Lord Azout as follows:
"…on the tip [of the worm's body] there is a
hole, through which the excrements can be excreted. On the other end there is a
larger hole, trough which the head can be protruded.
They are entirely black, the body shows
various segments, near the head there are three legs, each has two joints, not
dissimilar to these of a flea.
When they move their body is suspended in air,
the mouth but is still oriented to the rock. The head is bulky, a bit smooth,
similar in shape and colour to the shell of a snail...also the mouth is similar
large, with four kinds of teeth disposed in cross like manner."
The second engraving (Fig. 2) presumably shows the
stone worm in a more advanced state of development than in Fig. 1, as it is now
equipped with three pairs of legs. However, both forms seem only to possess
small, primitive, laterally-sited ocellus-like eyes (round and black, according
to de la Voye), rather than large, compound eyes, thereby indicating that if
the stone worm is an insect, as seems at least remotely possible, it is a
larval form rather than an adult (larval insects do not possess compound eyes,
only ocelli).
Conversely, some authors have sought to discount
the stone worms as (very) fanciful representations of funnel-weaving spiders,
three pairs of legs rather than four notwithstanding and the stone worms'
reputed rock-devouring proclivities discounted as apocryphal. Perhaps the
presence of multiple ocelli, a characteristic of many spiders (which never
possess compound eyes like most adult insects do), influenced their choice of
an arachnid identity for these creatures, as there seems little else that would
have done so? Certainly, the heavily segmented abdomen of the creature in the
second engraving, and the seemingly limbless, shelled form of the creature in
the first one, present major problems in reconciling them with any spider.
To be honest, however, the creatures depicted in
these two engravings are so bizarre that it is impossible to identify them
confidently with any known animal form. If they were indeed real, and not a
hoax perpetrated by de la Voye, we can only assume that these engravings are
exceedingly fanciful representations, so much so that the worms' true
morphology has been enshrouded in exaggeration or error.
As for their stone-devouring diet, this too is
baffling in the extreme. Perhaps de la Joye saw these creatures amid the wall's
crumbling masonry and wrongly presumed that they were responsible? Who can say?
All that can be stated is that except for a couple of brief mentions in some
early 18th-Century dictionaries of natural science, the stone worm
rapidly faded into total scientific oblivion shortly after Happel's book was
published.
Could it be that, as a monk, de la Voye was well-read
across a wide spectrum of religious tracts, was therefore familiar with the mythical
shamir from Jewish holy books, and had mistakenly thought that the creatures that
he had discovered were similar? In reality, however, even his stone worms'
ostensible comparability to the shamir does not stand up to close scrutiny. For
whereas the latter beast disintegrated and annihilated rocks using its formidable,
basiliskian gaze, the stone worm actually devoured rocks and stones, at least
according to de la Voye's testimony.
Almost 350 years have passed since de la Voye wrote
his intriguing letter documenting the stone worms, but its subjects remain as
mystifying and as unsatisfactorily 'explained' today as they were then. Unless
the entire episode of their discovery was indeed a hoax and a nonsense, the
stone worms must have been something – but what?
The second of two engravings of a
medieval and highly mysterious stone worm contained within a late 17th-Century
book by Eberhard Werner Happel



























The carvings in the Royston Cave in Hertfordshire UK are being eaten by little chalk eating worms - strange but true...
ReplyDeleteLuffia ferchaultella
ReplyDeletehttp://www.ukmoths.org.uk/species/luffia-ferchaultella/final-instar-larva/
This was a fable based upon the fossilized worms they would find in the rocks.
ReplyDeleteWow. Your way of maneuvering down rabbit holes to find the good stuff is inspirational. I am here because I was going down a really weird rabbit hole involving mandrake berries being called "jinn eggs" at some point, which made me explore the connection between jinn and mandrake. More recently I heard that another nickname for mandrake was "devil's candle", which some have said was because of all the lampyris noctiluca glow worms that gather on it to mate. So then I really went berserk and started reading stuff about glow worms and jinn or any kind of worms in relation to jinn and devils.
ReplyDeleteSo then it got even weirder and I started losing faith in the grail quest until I stumbled upon some kindred spirits here, bless y'all for that!
My thing is that the glow worm larvae eat snails and can use acid to dissolve portions of their shells, they glow greenish, they lived in the Israel area a long time ago, they are freaky and hard to miss, and they have the weird larval form with the six adult looking insect legs, also the jinn and Solomon are connected directly and the mandrake and the glow worm are connected and the worms and the jinn are connected, is there perhaps a link between it all?
Love to hear your thoughts!